The net costs and benefits of using professional medical interpreters
There are US patients with limited English proficiency (LEP), as well as international patients with LEP. With both types of patients, their communication with healthcare professionals and their general experience with the healthcare industry is marginalized.
From the point of view of a hospital, this means more patient visits, longer length of stays, and higher readmission rates – all of which mean higher costs for either the healthcare center or the patient with LEP. From a business point of view, these additional costs may be justified only if the additional revenue covers them. The solution to this is interpreting services, which come with their own direct and indirect costs. The natural question to ask is, is it worth it? Under what circumstances? When is it not worth it?
In this article, we provide a framework for answering these questions, and use an example to show how it works.
We begin by first defining all costs:
- General Hospital Costs
- Inpatient
- Readmission
- Outpatient
- Interpreter Costs
Costs will be calculated per average appointment, which will be a ratio of inpatient and outpatient appointments. Readmission will be calculated only for inpatient appointments. We end by subtracting financial benefits to come to a net cost analysis. We also calculate what the interpreter cost needs to be in order to break-even, as well as two scenarios (0% inpatient, and 0% outpatient) to understand when the cost outweighs the benefits, and when the benefits outweigh the cost.
General hospital costs
General hospital costs will be defined as costs that occur regardless of the level of English proficiency of a patient and any effects they have. In our model, we will group all relevant costs into three types:
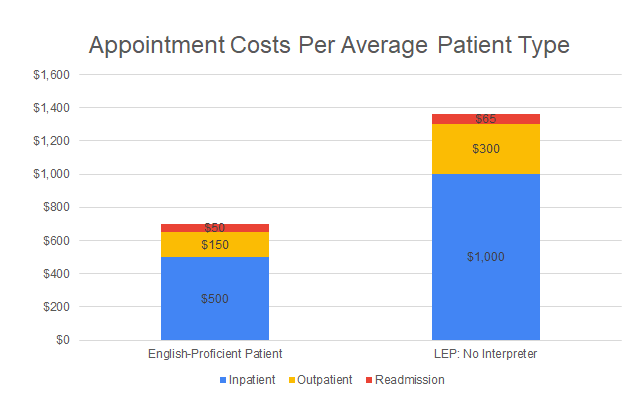
- Inpatient cost per day: All costs for having a patient stay one night at the healthcare facility. This will be set at $2000/day in the model, however, only 25% of patients will be assumed to be inpatients, so the average cost per patient or $500. Each inpatient is assumed to need only one appointment to be admitted, so the cost can also be interpreted as $500/appointment. For LEP patients, length-of-stay (LOS) can be longer by 2 days. This model will assume an LOS increase of only one day, which increases inpatient costs to $1000/appointment.
- Readmission costs: 30-day readmission cost as a function of the 30-day readmission rate. The cost and rate are set at $2000 and 10% in the model, respectively, which is applied only to inpatients, for an average of $50 per patient or appointment. For LEP patients, readmission rates increase by an average of 30%, to 13%, for an average cost of $65 per appointment.
- Outpatient appointment cost: Average cost per 15-minute time slot. This will be set at $200 per slot or appointment – applied to the remaining 75% of patients, which leads to an average cost per patient of $150. For LEP patients, the duration of time is doubled, for an average appointment cost of $400, which is an average of $300 for all appointments.
To start, the average cost per English proficient (EP) patient appointment is $700, compared to an LEP patient, which is $1,365. Not all costs may be relevant to every organization. For example, adjustments can be made for organizations that do not handle inpatients. This will be considered below.
Interpreter costs
Interpreter costs can be both direct or indirect. Two costs, the unfilled appointment rate and no-show rate, vary by interpreter and interpreting agency. In general, both rates are inversely associated with cost, as the main reason interpreter requests go unfilled is because a higher-paying appointment was confirmed. To account for this, we will look at two interpreter scenarios: low-cost provider (LCP) and high-quality provider (HQP). In total, there are three interpreter costs that will be considered:
- Interpreter hourly cost: When an interpreter is used, there is typically a per-hour charge, with a minimum of 2 hours. This is set to be $33 and $133 per hour for the LCP and HQP, respectively, for a total of $66 and $266 per appointment, respectively.
- Appointment fill rate: If an interpreter request cannot be fulfilled, there is usually a cost associated with it in the form of a healthcare professional’s time. This is set to be 55% and 95% for the LCP and HQP, respectively.
- No-show rate: The unfilled appointment cost is higher if the interpreter was successfully reserved but does not show up to the appointment (even adjusting for not paying the interpreter). This is set to be 20% and 5% for the LCP and HQP, respectively.
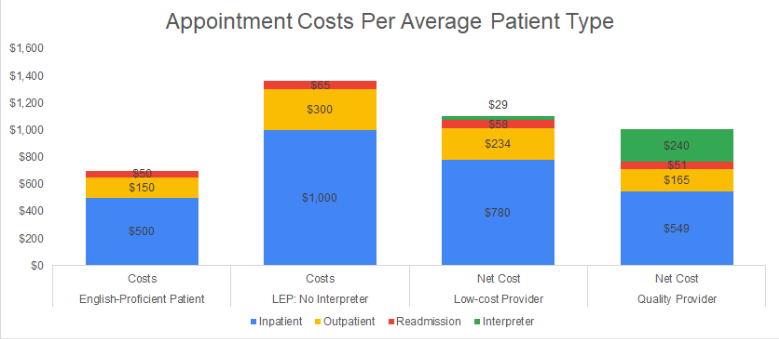
Adjusting for the appointment fill rate and the no-show rate, the LCP and HQP interpreter per-appointment costs decline from $66 to $29 and from $266 to $240, respectively.
Cost effects from using an interpreter
Since hospital costs, including healthcare professionals, are typically higher than direct interpreter costs, hospital costs associated with unfilled appointments and no-shows can be higher than the interpreting costs themselves.
For inpatient costs per appointment, length of stay is assumed to return to normal on the occasion when the interpreter arrives to the appointment. On average the inpatient costs reduce from $1000 to $780, and from $1000 to $549 for the LCP and HQP scenarios, respectively.
For outpatient costs per appointment, slot costs are assumed to return to normal on the occasion when the interpreter arrives to the appointment. On average, the outpatient costs per appointment reduce from $400 to $312 and from $400 to $220 for the LCP and HQP scenarios, respectively.
For readmission costs per appointment, readmission rates are assumed to return to 10%, reducing readmission costs from $65 to $58 and from $65 to $51 for the LCP and HQP scenarios, respectively.
The average EP patient costs a hospital $700 per appointment. LEP patients increase the average inpatient, outpatient and readmission costs by a total of $665 for a net cost of $1,365. When an interpreter is used, these same costs decline by $293 to $600 (depending on the LCP and HQP scenario, respectively), for a net cost of $1,072 to $765. In other words, interpreting costs would need to be between $293 and $600 in order for the effect of the interpreter to be negated, and for their costs to break-even against their benefits. Furthemore, there are additional benefits of using an interpreter that are not measured, such as improved patient and medical staff satisfaction ratings and the medicare reimbursements associated with improved patient satisfaction. Finally, better communication between medical staff and patients improves treatment adherence, success rates and additional medicare reimbursements associated with improved readmission rates.
No inpatients scenario
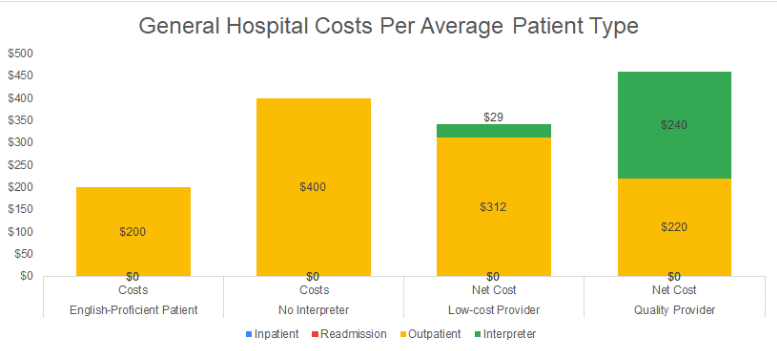
LEP patients increase the average inpatient, outpatient and readmission costs by a total of $200 for a net cost of $400. When an interpreter is used, these same costs decline by $88 to $180 (depending on the LCP and HQP scenario, respectively), for a net cost of $312 to $220. In other words, interpreting costs would need to be between $88 and $180 in order for the effect of the interpreter to be negated, and for their costs to break-even against their benefits.
No outpatients scenario
LEP patients increase the average inpatient, outpatient and readmission costs by a total of $1000 for a net cost of $3000. When an interpreter is used, these same costs decline by $479 to $982 (depending on the LCP and HQP scenario, respectively), for a net cost of $2,741 to $2,238. In other words, interpreting costs would need to be between $479 and $982 in order for the effect of the interpreter to be negated, and for their costs to break-even against their benefits.
If you’d like to learn more about how BURG Translations helps you ensure high quality medical interpretations, contact us today.